Monitoring specific process-related impurities
During development and manufacturing, residual proteins derived from production, such as Host Cell Proteins (HCPs), growth factors, serums, and processing reagents, must be monitored through each downstream purification step to ensure efficient clearance and purity of the final drug substance. Residuals may cause unwanted biological activity, immunogenicity, or degradation of the therapeutic protein or polysorbate surfactants.
Alphalyse offers development of targeted liquid chromatography mass spectrometry methods (LC-MS). Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM) analysis is a highly specific and sensitive LC-MS technique that can target your residual protein(s) of interest in both the final drug product and individual process samples. MRM enables a low-to-sub ppm detection limit and is advantageous for identifying and quantifying key residuals, even in complex process samples.
Why use LC-MS for process-related impurity analysis?
Document and monitor process-derived residuals
Quantify target proteins throughout the purification process and in the final drug substance
Full validation of assay under GMP
Fully validate your assay according to ICH guidelines for use as a release assay under GMP
Assay targeting polysorbate-degrading HCPs in mAbs
Our standard assay targets the most common lipases and esterases found in monoclonal antibody products
Regulatory authorities demand documentation for the efficiency of downstream purification of specific enzymes and proteins added during process development to ensure patient safety, drug stability, and efficacy.
Mass spectrometry analysis can detect all types of process-related protein residuals, e.g., affinity capture chromatography proteins, growth factors, Benzonase® nuclease, Protein A, enzymes for site-specific PEGylation, aminopeptidase, serum albumin, cytokines, protein-based media components, carrier proteins, and more.
Using LC-MS analysis with Multiple Reaction Monitoring (MRM), unique signature peptides for specific proteins can be identified and quantified even in small amounts. The assay is highly reproducible and, therefore, ideal for batch-to-batch comparison.
The LC-MS assay can be fully validated according to ICH guidelines and performed under GMP conditions as a release assay if needed.
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) has been the gold standard in the industry for HCP analysis for many years. However, it is restrained by a lack of specificity and a limited possibility to monitor multiple specific proteins in highly complex samples. Developing a process-specific ELISA is time-consuming and typically takes 1 to 1.5 years.
A customized mass spectrometry (LC-MS) assay for MRM analysis can be developed and validated within six months. It may quantify even low amounts of specific proteins utilized during manufacturing.
We can measure up to 20 individual proteins in the same LC-MS run using multiplex analysis. The technique is highly reproducible and provides both the identity and absolute amounts of specific analytes. Furthermore, the method can be validated and qualified according to your specifications.
Polysorbate surfactants are crucial to the shelf-life and efficacy of monoclonal antibody (mAb) products, and their degradants may form particles that are harmful to patients and considered a critical quality attribute outlined by the USP General Chapters <787> and <788>. Consequently, degradation of polysorbates is a major problem in mAb development, resulting in project delays, often in very late stages of project development.
While some host cell proteins (HCPs) – such as proteases that cleave the therapeutic protein – are usually found early on, polysorbate-degrading lipases and esterases can remain undetected in the final drug product until months or years into long-term stability studies – or even after the product has been licensed!
At this stage, modifying the manufacturing process to eliminate these elusive yet dangerous HCPs is costly and time-consuming. Identifying polysorbate-degrading HCPs in a mAb product before they become a problem is the most effective way to reduce their impact on the project timeline.
Video case
Do you experience polysorbate degradation – but don’t know the cause?
One of our mAb clients struggled with polysorbate degradation, affecting the efficacy and safety of their drug product. The client suspected the problem was a host cell protein – a lipase – which co-purified with the mAb through Protein A purification. But without knowing the identity or characteristics of the culprit, they were unable to remove it from the final drug product.

Typical project process
You typically work with
these experts:


Project scope
We like to start with an online meeting to learn more about your project. Based on your needs, you will receive a draft proposal outlining the suggested analyses and expected timeframe. We will develop the MRM LC-MS analysis specifically for your protein and project.
Samples
After signing the final project proposal, we will contact you for details about your samples. We will inform you of an estimated report delivery date as soon as we receive your samples.
Execution
A project leader will oversee the project and send you status updates by email at regular intervals.
A typical analysis includes:
- Identification of up to 3 unique signature peptides for each protein for quantitation.
- Standard curves and linearity assessment for a dilution series of the quantification standards and, if possible, the residuals in your specific samples.
- Absolute quantification of the proteins of concern by MRM LC-MS.
- Reporting of the determined protein amounts and analysis details.
Results
You will receive the report by email, the analysis report includes:
- Objectives, description of analytical procedure, results, and conclusions.
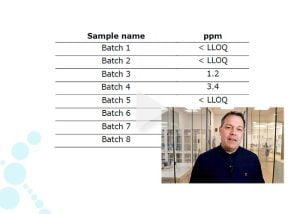
- List of identified and quantified impurities in each sample.
- Selected raw data, e.g., excel sheets. Additional raw data may be provided to you upon request.
Follow up
Upon completion of the project, your team is invited to go through the results at an online meeting.
Curious to know more?

Whatever challenge or question you may have, we are here to help you solve it. One of our protein analysis experts will discuss the best analysis approach or method for your project by email or online meeting – without obligation.
Client stories
Video: Residual biocatalysis in small molecule API
Analysis of individual human residual proteins
Quantifying lentivirus and residual proteins in one assay
Comparing viral protein quantities in AAV batches and DS
Analyzing heterogeneous HCP mix from multiple species
The advantages of LC-MS MRM analysis of residual proteins
Fast development of a protein-specific assay
Highly sensitive – sub-ppm level
Extensive dynamic range – up to 4-5 orders of magnitude
Accurate and reproducible quantification in very complex samples
Can be fully validated accordingly to ICH guidelines and used as a release assay under GMP
Multiplexing for monitoring up to 20 proteins in one assay
What clients say
Knowledge center
How can HCP quantitation using LC-MS be validated?
We can fully validate our MRM method as a quantitative method for the specific impurities and product according to ICH guidelines. Reproducible quantitation of HCPs in the samples is obtained using a robust, automated sample preparation method and adding intact protein standards for normalizing the data. SCIEX services the LC-MS system for installation and operational qualifications (IQ, OQ), and our laboratory procedures are meticulously set up and audited for regulatory compliance with GMP requirements.
Regulatory compliance can be complex, time-consuming, and costly. Alphalyse offers you the option of saving time and resources by contracting our expert team and top-of-the-line instrumentation for validated analyses.
Which database do you use to search for peptide information? Are there any GMP compliance issues with using protein databases?
We typically pull databases and proteomes from UniProtKB. In addition, we can use your custom host cell strain database if available. Several databases are often combined to ensure the inclusion of all potential proteins. Since we rely on publicly available protein databases, no GMP compliance issues exist.
How do you calculate impurity results in ppm when using LC-MS?
We know the exact amount of each of the seven intact protein standards spiked into the sample of known volume and protein concentration. Therefore, we can use the median response curve of the protein standard to calculate the ppm amount of each host cell protein from its total mass spec signal intensity (sum of all peptides).
Research article:
Videos:
- Analysis of residual protein in viral products
- Target protein detection
- Residual biocatalysis in API
- Monitoring process added enzymes using an MRM assay
Cases:
- Quantifying lentivirus and residual proteins in one assay
- Analysis of individual human residual proteins using an orthogonal method
- Analyzing heterogeneous HCP mix from multiple species
Infographic:
Talk to us
Whatever protein-related challenge or question you may have, we would love to help. Our experts can help you decide on the best analytical approach for your project by email or online meeting - providing advice without obligation.